Introduction: What are ceramides?
Ceramides are a special group of skin-identical lipids that play a central role in human skin health. As the “cement” between the corneocytes (corneocytes), they form the basis of the skin barrier – the invisible protective layer that protects our skin from moisture loss, pollutants, and pathogens. Without ceramides, our skin would be dry, sensitive, cracked, and prone to numerous dermatological problems.
In cosmetic products, ceramides are now among the most popular active ingredients for all skin types – especially for dry, sensitive, mature, or barrier-damaged skin. In this article, we show you what ceramides are, what types there are, how they work, and where they are used effectively in modern skin care.
Ceramides in the skin and their biological significance
Ceramides make up about 50% of the intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum (the uppermost layer of the skin). They consist of a fatty acid and a sphingoid base – together they form a waxy substance that fits tightly between the corneocytes.
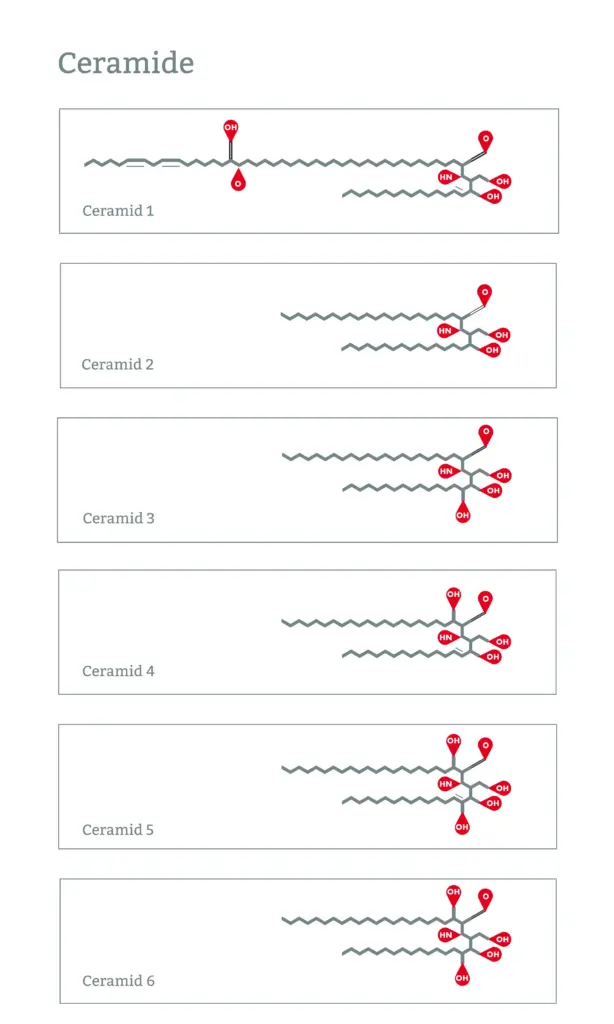
A total of nine main types of ceramides have been identified in human skin. These are usually designated by Roman numerals in the cosmetics industry:
- Ceramide 1 (EOS)
- Ceramide 2 (NS)
- Ceramide 3 (NP)
- Ceramide 4 (EOH)
- Ceramide 5 (AS)
- Ceramide 6-II (AP)
- Ceramide 7 (AH)
- Ceramide 8 (NH)
- Ceramide 9 (EOP)
These different types perform slightly different tasks in the skin barrier. Ceramides 1, 2, 3, and 6-II are particularly important for the protective function and moisture retention.
Extraction and production
In nature, ceramides occur in human skin, in animal sources (e.g., milk) and in certain vegetable oils. For cosmetic products, ceramides are usually produced biotechnologically for ethical and practical reasons. This is done by fermentation with yeast or by enzymatic synthesis from vegetable oils such as soybean or rice germ oil.
The result is so-called pseudo-ceramides or skin-identical ceramides, which are exactly modeled on the human structure and are therefore particularly well tolerated and effective.
Advantages of ceramides in cosmetics
Ceramides are true all-rounders in skin care. Their most important advantages:
Barrier formation & protection
- Ceramides form a protective matrix in the skin and prevent water from evaporating or harmful substances from penetrating.
Moisture retention
- Especially in combination with moisture-binding active ingredients such as glycerin or urea, ceramides prevent dry and flaky skin.
Soothing effect
- They relieve redness, itching, and irritation—ideal for neurodermatitis, rosacea, or psoriasis.
Anti-aging effect
- A strong skin barrier reduces oxidative stress and strengthens the skin structure, reducing lines and wrinkles.
Strengthening the hair coat
- Hair also benefits from ceramides: they smooth the hair structure, increase resilience and make hair more supple.
Disadvantages and challenges
Despite their many advantages, there are some limitations to the use of ceramides:
High raw material costs
- Biotechnological production is complex and makes ceramides one of the more expensive active ingredients in the cosmetics industry.
Formulation requirements
- Ceramides require special carrier systems (e.g., liposomes or lamellar cream structures) to be able to develop their full effect.
Stability & processing
- Ceramides are sensitive to pH changes and high temperatures, which must be taken into account during production.
Effectiveness: What do studies say?
Numerous studies confirm the clinical effectiveness of ceramides, especially in skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, ichthyosis, and psoriasis.
A remarkable result was shown in a study in which a cream containing 1% ceramides (a combination of types 1, 3 and 6-II) was used. After just 4 weeks of regular use, skin moisture improved significantly, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) was significantly reduced, and the skin appeared smoother and more resilient.
Positive effects were also observed in hair care: ceramides can restructure the outer layer of the hair, prevent split ends, and improve combability.
Physical and chemical properties (example: Ceramide NP)
INCI name: Ceramide NP
Alternative names: Ceramide 3, N-stearoyldihydrosphingosine
Molecular formula: C42H83NO3
Appearance: White, waxy powder or granules
Physical state: Solid
Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in oils
Melting point: approx. 90–95 °C
Production: Biotechnologically produced from plant lipids
Product ideas for the use of ceramides
Ceramides are extremely versatile and can be used in numerous cosmetic formulations:
Barrier protection cream for dry to atopic skin
Combination of ceramide 1, 3, 6-II with panthenol and urea to stabilize the skin barrier.
Anti-aging night care
Rich formula with ceramides, retinol, and hyaluronic acid for skin renewal while you sleep.
Hair mask with ceramides
Ceramides 2 and 3 to repair brittle hair, combined with keratin and plant oils.
After-sun lotion
Ceramide 6-II to regenerate sun-damaged skin, with aloe vera and vitamin E.
Lip Repair Balm
Ceramide 3, plant waxes, and shea butter for intensive care of chapped lips.
Body lotion for sensitive children’s skin
Light emulsion with skin-identical ceramides, without perfume or alcohol.
Conclusion
Ceramides are not just a hype, but a scientifically proven skin care ingredient with enormous potential. Their ability to specifically repair and strengthen the skin barrier makes them an indispensable component of modern cosmetic formulations. Whether for dry skin, neurodermatitis, mature skin or damaged hair – ceramides are true all-rounders.
We use the active ingredient ceramides described above in our high-quality private label products, which meet the highest standards of effectiveness, skin compatibility, and innovation. We combine proven ingredients with modern biotechnological developments to create tailor-made formulations that meet the individual needs of your target group. Our focus is on quality, transparency, and the optimal synergy of all ingredients – for visible results and a compelling brand experience.
Tojo Cosmetics Private Label – your brand, our passion for effectiveness and quality.
Interested? Contact us now with no obligation.
Literature:
A daily regimen of a ceramide-dominant moisturizing cream and cleanser restores the skin permeability barrier in adults with moderate eczema: A randomized trial.; Spada F, Harrison IP, Barnes TM, Greive KA, Daniels D, Townley JP, Mostafa N, Fong AT, Tong PL, Shumack S.Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jul;34(4):e14970.
Enhancing Skin Health: By Oral Administration of Natural Compounds and Minerals with Implications to the Dermal Microbiome.; Vollmer DL, West VA, Lephart ED. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 7;19(10):3059.
Skin lipids in health and disease: A review.; Knox S, O’Boyle NM. Chem Phys Lipids. 2021 May;236:105055.
Clinical significance of the water retention and barrier function-improving capabilities of ceramide-containing formulations: A qualitative review.; Kono T, Miyachi Y, Kawashima M.J Dermatol. 2021 Dec;48(12):1807-1816