Introduction
In modern cosmetics, the demand for effectiveness, skin compatibility, and innovation is higher than ever before. Consumers expect products that not only care for their skin, but also specifically address its needs. Acetylglucosamine (NAG for short) is one such active ingredient – it combines scientifically proven efficacy with excellent skin compatibility and multifunctional applications. In this article, you will learn everything about this exciting raw material: its origin, properties, benefits, efficacy, and areas of application.
Origin and occurrence in nature
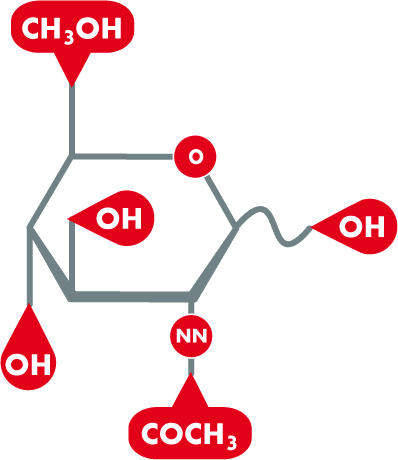
Acetylglucosamine, also known as N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, is a naturally occurring amino sugar and a derivative of glucose. It is an essential intermediate product in human metabolism and is a component of hyaluronic acid, among other things—a substance produced naturally by the body that contributes significantly to skin moisture. In nature, acetylglucosamine also occurs in structural biopolymers, particularly in chitin, which is found in the shells of crustaceans (e.g., shrimp, crabs), fungi, and the cell walls of certain bacteria.
Commercially, acetylglucosamine is usually produced from chitin using biotechnological processes. Chitin is hydrolyzed enzymatically or chemically to achieve high purity and quality.
Production methods
There are two main processes for obtaining acetylglucosamine:
- Chemical hydrolysis of chitin (usually from crustacean shells): Here, chitin is broken down into its monomers, in particular NAG, by treatment with acid.
- Enzymatic hydrolysis with chitinase and chitosanase: This process is more environmentally friendly, more selective, and enables production in pharmaceutical quality.
More recent approaches are increasingly focusing on fermentative biotechnological production, in which microorganisms are used to produce NAG in a targeted manner. This method is particularly sustainable and vegan-friendly.
Advantages of acetylglucosamine in cosmetics
Acetylglucosamine has a number of skin-relevant properties that make it a highly interesting cosmetic ingredient:
Promotes the body’s own hyaluronic acid production
Acetylglucosamine is a direct building block of hyaluronic acid. Topical application can stimulate the skin to increase its own production of hyaluronic acid, which leads to increased skin moisture and improved skin elasticity.
Reduction of hyperpigmentation
Acetylglucosamine inhibits the activity of the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for the formation of melanin. This reduces the appearance of pigment spots (e.g., caused by UV damage or acne scars).
Improvement of skin structure
NAG has keratolytic properties: it weakens the bond between dead skin cells in the stratum corneum, resulting in gentle exfoliation. Unlike AHA or BHA, this effect is much gentler on the skin, making it ideal for sensitive skin.
Anti-aging effects
Acetylglucosamine intercepts free radicals caused by UV radiation and protects skin cells from oxidative stress. Its antioxidant effect helps to slow down skin aging.
Moisture retention
As a sugar derivative, NAG itself has hygroscopic properties. It helps to bind water in the skin, supports the barrier function and ensures a smooth, hydrated complexion.
Disadvantages of acetylglucosamine
Despite its many advantages, there are also some aspects that need to be taken into account in the formulation:
- Animal source: NAG is traditionally derived from chitin found in crustaceans, which can make it problematic for vegan cosmetics or for people with shellfish allergies. (Alternative: biotechnologically produced NAG)
- More expensive production: Highly purified acetylglucosamine is more expensive than other active ingredients, which can affect the price of the final product.
- Stability: NAG should not be added to very acidic or strongly alkaline formulations, as this can impair the stability of the molecule.
Physical and chemical properties of acetylglucosamine
INCI name: Acetyl Glucosamine
CAS number: 7512-17-6
EINECS number: 231-165-9
Molecular formula: C8H15NO6
Molecular weight: 221.21 g/mol
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder
Physical state: Solid
Melting point: approx. 185 °C
Solubility: Water-soluble, insoluble in organic solvents
Synonyms: N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine, NAG
Effectiveness and recommended concentration
The effectiveness of acetylglucosamine has been scientifically proven and supported by various studies:
- A study by Kimball et al. (2010) showed that a combination of 2% niacinamide and 4% acetylglucosamine significantly contributes to the reduction of hyperpigmentation.
- In another study, a significant improvement in skin moisture, a reduction in pigment spots and gentle exfoliation were observed with just 1% acetylglucosamine.
- Combining it with hyaluronic acid further increases the skin’s moisture retention.
- At concentrations of 1–4%, acetylglucosamine is considered particularly effective and very well tolerated by the skin.
Application examples in cosmetic products
Acetylglucosamine is ideal for a wide range of cosmetic products, especially in the following categories:
Anti-aging creams and serums
- Supports hyaluronic acid formation and smoothes fine lines through intensive moisturization.
Brightening serums against pigment spots
- In combination with niacinamide, excellent against acne scars and UV-induced discoloration.
Moisturizing masks and night care
- Ideal for regenerating the skin barrier overnight.
Eye creams for dark circles and puffiness
- Brightens, soothes, and regenerates.
Exfoliators for sensitive skin types (rosacea, keratosis pilaris)
- Gentle exfoliation without acids – perfect for sensitive skin.
After-sun products
- Thanks to its antioxidant effect, ideal for soothing sun-stressed skin.
Conclusion: Versatile active ingredient with high potential
Acetylglucosamine is a highly effective ingredient that can play a central role in modern cosmetic formulations. Thanks to its diverse properties – from moisturizing and skin lightening to gentle exfoliation – NAG is a true all-rounder. The effect can be significantly enhanced when combined with niacinamide and hyaluronic acid. Due to its high skin compatibility, acetylglucosamine is also suitable for sensitive skin types and special applications such as after-sun or eye care products.
We use the active ingredient acetylglucosamine described above in our high-quality private label products, which meet the highest standards of effectiveness, skin compatibility, and innovation. We combine proven ingredients with modern biotechnological developments to create tailor-made formulations that meet the individual needs of your target group. Our focus is on quality, transparency, and the optimal synergy of all ingredients—for visible results and a compelling brand experience.
Tojo Cosmetics Private Label—your brand, our passion for effectiveness and quality.
Interested? Contact us now with no obligation.
Literature:
N-acetylglucosamine: production and applications.; Chen J; Shen C; Liu C. Marine drugs, 2010, 8. Jg., Nr. 9, S. 2493-2516.
Nanostructured Lipid Carrier for Topical Application of N-Acetyl Glucosamine.; Aliasgharlou L, Ghanbarzadeh S, Azimi H, Zarrintan MH, Hamishehkar H. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016 Dec;6(4):581-587.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color.; Davis EC, Callender VD.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010 Jul;3(7):20-31.
Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation after use of moisturizers with a combination of topical niacinamide and N-acetyl glucosamine: results of a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial.; Kimball AB, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 19845667 Clinical Trial.
Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation after use of moisturizers with a combination of topical niacinamide.; Randomized Controlled Trial 2010 Feb 1;162(2):435-41.
Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits.; Donald L Bissett. 2006. 5(4): 309–315.
Determination of N-acetylglucosamine in cosmetic formulations and skin test samples by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and UV detection.: Alice Pedrali, Mariella Bleve, Priscilla Capra, Tobias Jonsson, Gabriella Massolini, Paola Perugini, Giorgio Marrubini, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2015, 107. Jg.: 125-130.
Donald L Bissett. 2006. 5(4): 309–315.
Determination of N-acetylglucosamine in cosmetic formulations and skin test samples by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and UV detection. Alice Pedrali, Mariella Bleve, Priscilla Capra, Tobias Jonsson, Gabriella Massolini, Paola Perugini, Giorgio Marrubini, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2015, vol. 107: 125-130.